UD TRUCKS GWE370 Gearbox Component
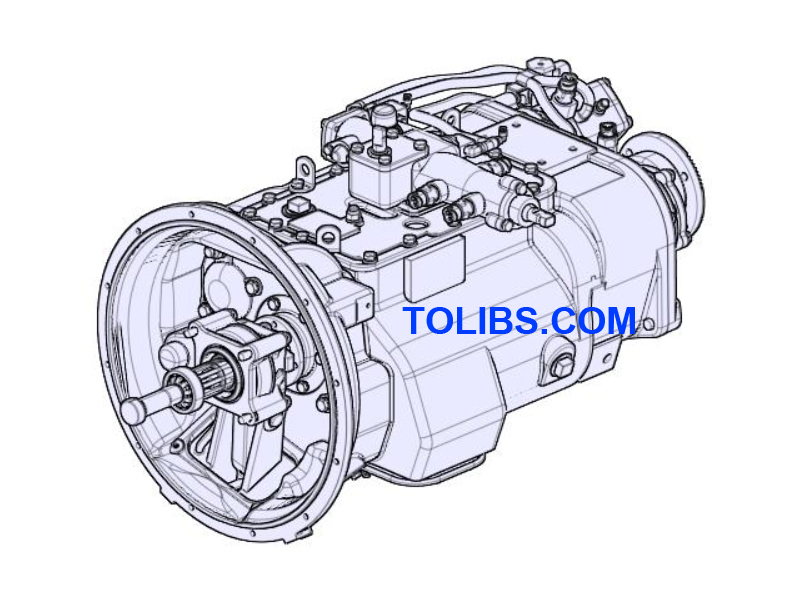
UD TRUCKS GWE370 Gearbox Mechanical Component Description
The gear box is a 12 speed, in which 12 forward gears are fully-synchronised and 2 reverse gear is unsynchronised. The gearbox combines a design of main and auxiliary case, the main case is manually controlled and auxiliary case is pneumatic control. The gearbox is a range group of planet gears with 12 fully synchronised forward gears and an unsynchronised 2 reverse gear.
Terminology
- Type: STO2012 (12 speed)
- Symbols:
- S: Synchronised
- T: Transmission
- O: Overdrive
Power take-off variants
A clutch-dependent PTO (Power Take-Off) can be connected to the gearbox for different superstructures.
| Variant symbol | Variant description |
| PTOTRA-S | Single PTO transmission |
| UPTOTRA | Without PTO transmission |
| PTR-F | Rear PTO transmission, Flange, 100% speed |
| PTR-D | Rear PTO transmission, DINCONN, pump |
Housing
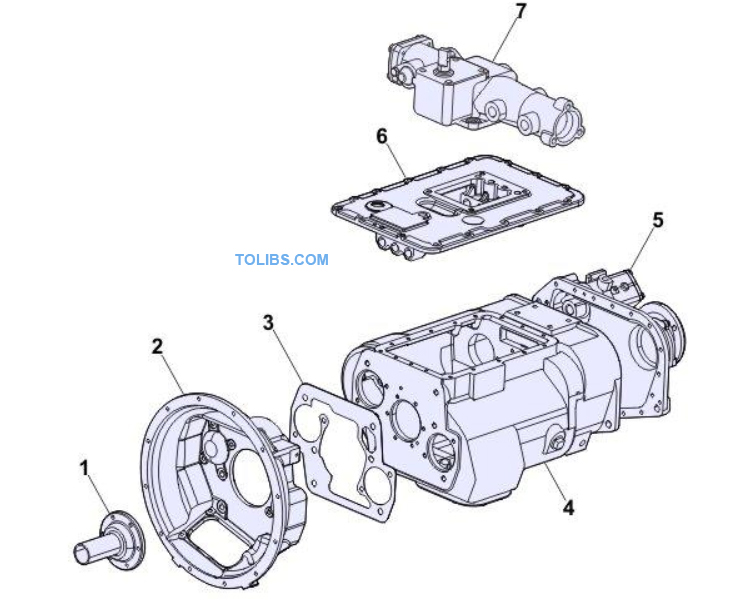
- Bearing cover
- Clutch housing
- Gasket
- Main housing
- Range housing
- Top cover
- Control housing
The main sections of the gearbox are the clutch housing (2), main housing (4), range housing (5) and control housing (7). The clutch housing (2) contains the input shaft as well as clutch servo. The main housing (4) contains the main shaft, intermediate shaft, reverse shaft and shift mechanism. The range housing (5) contains the planetary gears, shift mechanism, actuator and output shaft.
Internal Parts
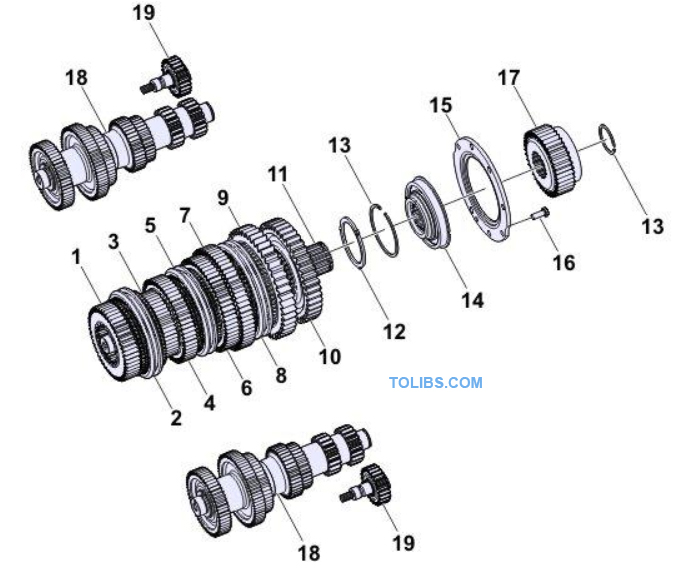
- 5th gear
- Synchronizer assembly
- 6th gear
- 4th gear
- Synchronizer assembly
- 3rd gear
- 2nd gear
- Synchronizer assembly
- 1st gear
- Reverse gear
- Main shaft
- Spacer
- snap ring
- Bearing assembly
- Retainer
- Hexagonal bolt
- Auxilary drive gear
- Countershaft assembly
- Reverse gear
Input shaft
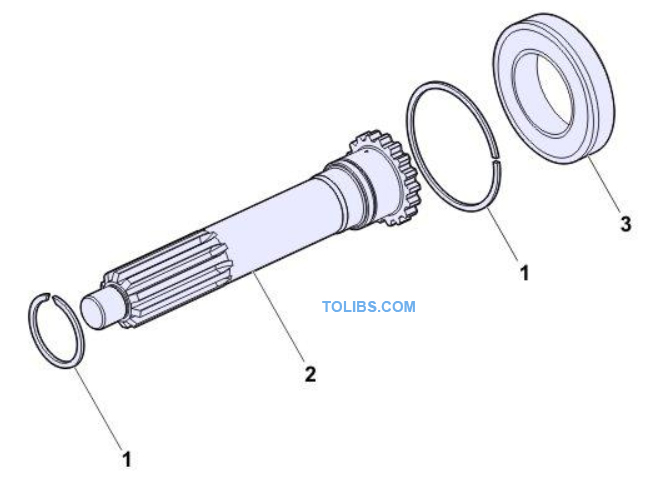
- Snap ring
- Input shaft
- Bearing
The input shaft transfers the engine power to the gearbox via the clutch disc. Note: The input shaft always rotates in a clockwise direction (viewed from the front).
Counter shaft
The front and rear end of the Counter shaft is mounted in the bearings. Each countershaft transfers half torque.
The advantage of the countershafts are:
- It reduces the gear width.
- It reduces the size and weight of the transmission
Main shaft
Both ends of the main shaft are mounted in bearings. The front end is mounted in the end of the input shaft, whereas the rear end is mounted in the rear of the main housing.
Output shaft
The output shaft is mounted in the range housing with roller bearing and is linked to the range gear. Note: The cross-tooth flange is standard for all types of gearbox.
Reverse gear
There are two reverse gear which is meshed to the two countershaft. The reverse gear changes the direction of the rotation, which allows the vehicle to move in reverse direction.
Synchronization

- Synchronizer sleeve
- Locate ring
- Spring
- Synchronizer hub
- Outer synchronizer ring
- Double cone synchronizer
- Gear clutching teeth
- Inner synchronizer ring
The synchronizer in the transmission makes shifting easier and more convenient, it reduces collision and noise. Using synchronizer the gear’s life and performance can be increased. Except the reverse speed gear, other gears are equipped with synchronizers.
Range gear
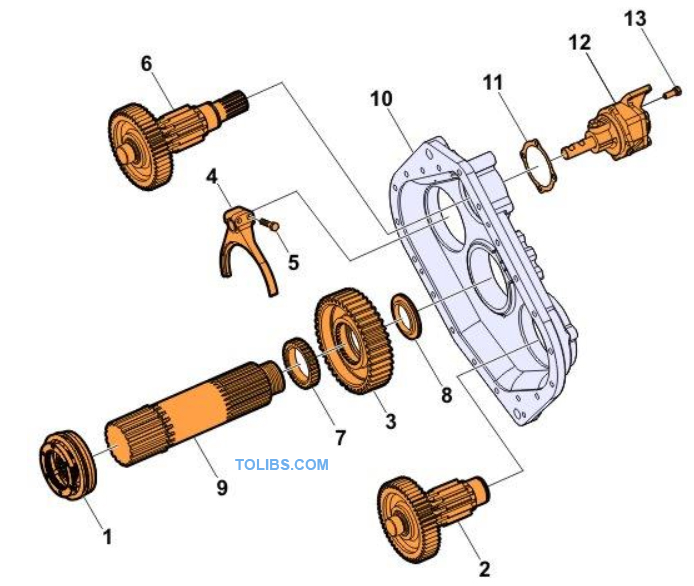
- High speed synchronizer
- Auxiliary counter shaft
- Reduction gear on main shaft auxiliary case
- Yoke, Auxiliary case
- Hexagonal bolt
- Auxiliary lengthened countershaft
- Speedo meter pulse ring
- Baffle plate, main shaft gears
- Main shaft, auxiliary case
- Rear cover
- Sealing gasket
- Auxiliary shift cylinder
- Hexagonal bolt
The range gear or auxiliary gear is installed behind the main case. The input shaft of the auxiliary unit is connected directly to the output shaft of the primary gear case.
Gearbox selection Control housing
Without inhibitor
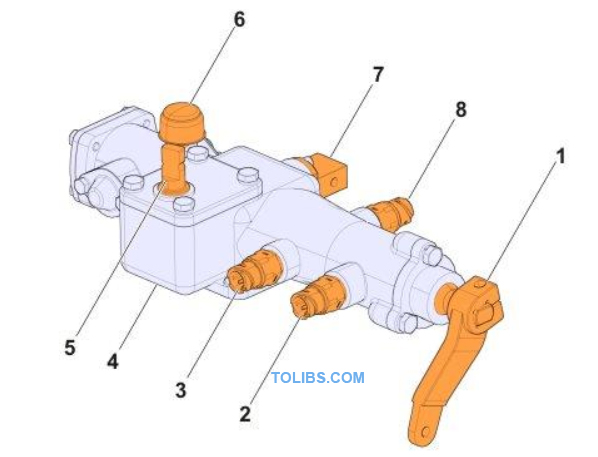
- Shift cable joint
- Neutral sensor
- Reverse sensor
- Control housing
- Selector cable joint
- Breather
- Control valve
- Reverse sensor
With inhibitor
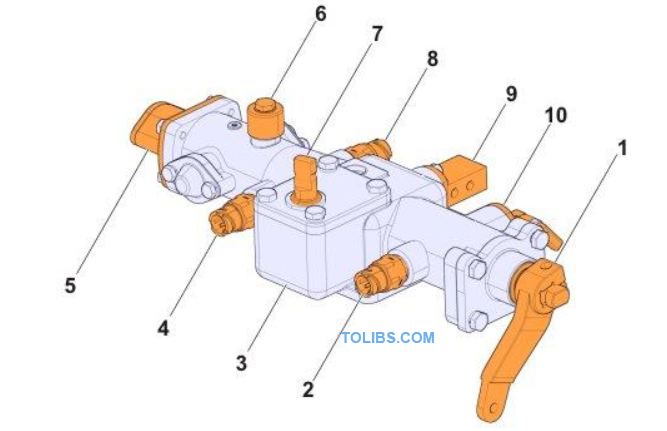
- Shift cable joint
- Reverse sensor
- Control housing
- Neutral sensor
- Inhibitor actuator
- Breather
- Selector cable joint
- Reverse sensor
- Control valve
- Interlock Actuator
The control housing is located on the top of the gearbox and it is intended to transfer the motion of the gear lever to the gearbox shift rods. The position of the control housing can be adjusted for both left and right hand drive truck variants. The control housing consists of a gear selector to which is secured a selector shaft. The gear selector is controlled by a gear selector cable and a side control cable.
Gearshift cable
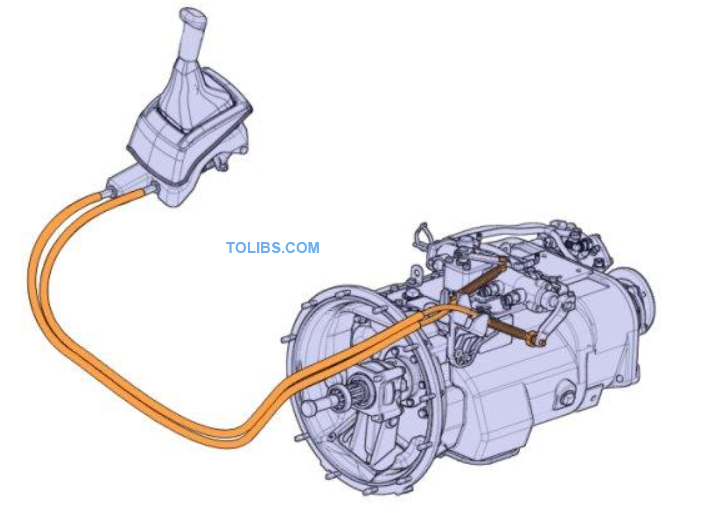
The cable gear shift system has two cables that is shift cable and select cable, which transfer force between the gear lever and the control housing on the gearbox.
Gear shift
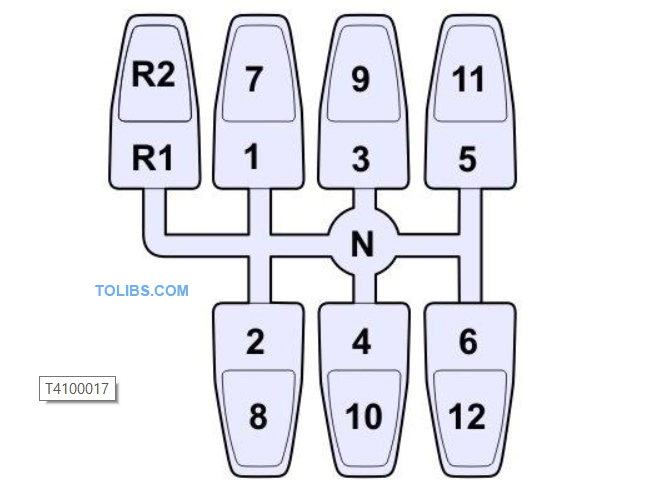
The range gears at the rear of the gearbox double the number of gears in the synchronised section. There are totally of 12 forward gears, Gears 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 are low range and gears 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 are high range.
The gear change gate has 3 parallel gear selection paths. In the path between gears 3/4 and 9/10 is a spring-loaded neutral position. The pneumatic range changes from 3 to 4 and from 5 to 6, and vice versa, are selected by pressing the button on the side of the gear lever.
There are zone, range and reverse blocking functions to protect the synchronisation from being damaged while changing gear. The zone block prevents changing into 1st gear by blocking 1st gear if the output shaft speed is too high. The range block prevents changing into the low range gears if the output shaft speed is not low enough. The reverse block prevents reverse gear selection if the main shaft and intermediate shaft are rotating, i.e. if the vehicle is not stationary












